1 前言
跳表(SkipList ) 又称跳跃表,是一种随机化的数据结构,可以视作二叉树的一个变种,它在性能上和红黑树,AVL 树不相上下,但是跳表的原理非常简单,在 Redis 和 LeveLDB 中都有用到。同时也是面试中的热门问题。
2 原理与实现
2.1 介绍
跳跃表 (简称跳表) 由美国计算机科学家 William Pugh 发明于 1989 年。他在论文《Skip lists: a probabilistic alternative to balanced trees》中详细介绍了跳表的数据结构和插入删除等操作。
跳表 (SkipList,全称跳跃表) 是用于有序元素序列快速搜索查找的一个数据结构,跳表是一个随机化的数据结构,实质就是一种可以进行二分查找的有序链表。跳表在原有的有序链表上面增加了多级索引,通过索引来实现快速查找。跳表不仅能提高搜索性能,同时也可以提高插入和删除操作的性能。它在性能上和红黑树,AVL 树不相上下,但是跳表的原理非常简单,实现也比红黑树简单很多。
回顾链表,相对数组,链表的优点是高效的插入、删除,缺点是查询非常慢,复杂度达到 O(n)。
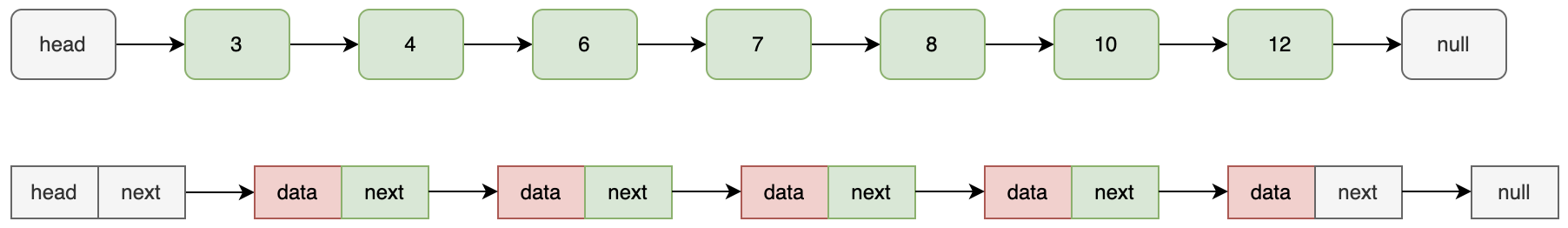
这是一个带头结点的链表(头结点相当于一个固定的入口,不存储具体的值),每次查询请求时,需要重头开始遍历每一个值。参考数组的二叉树遍历,是否可以在链表也能用类似的思想来遍历?以空间换时间,在单链表上增加一层索引,增加索引的范围,可以减少链表的查询时间。
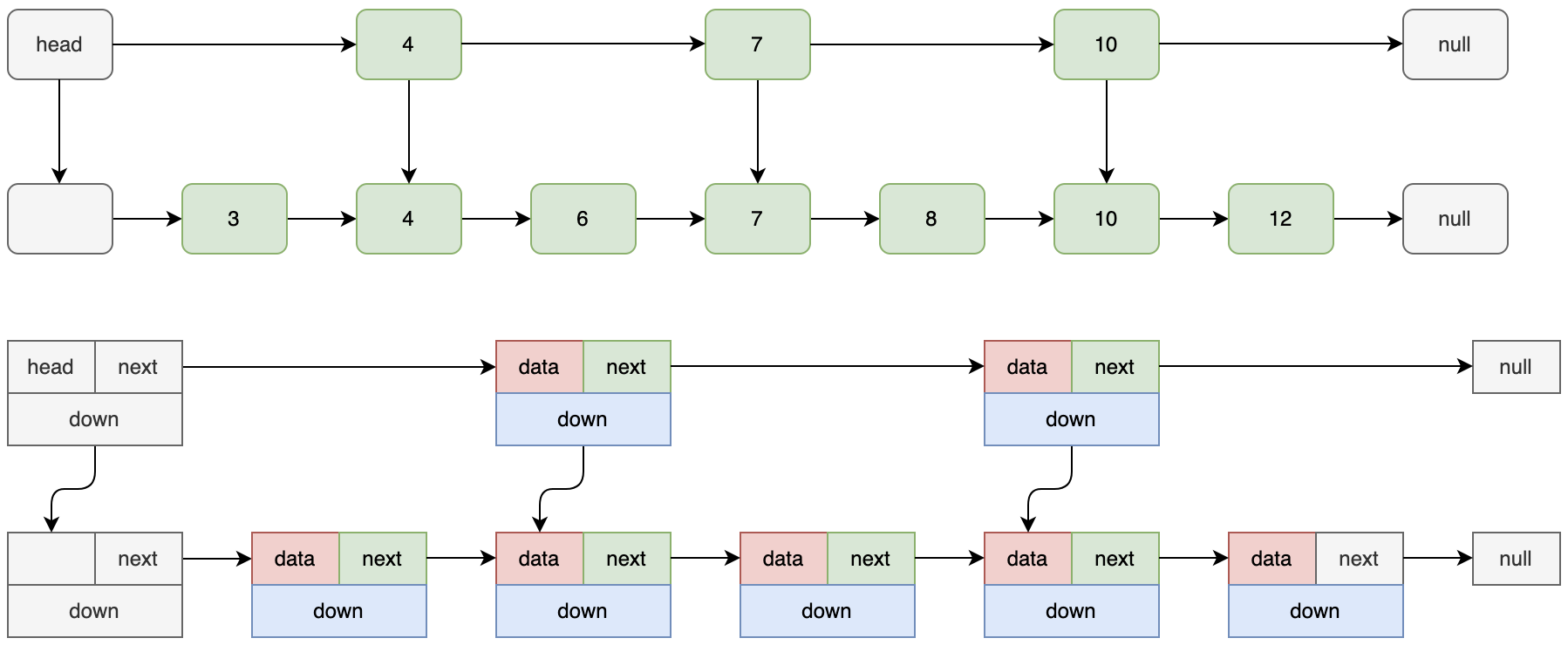
如上,在查询某个结点的时候,首先在上层索引中查找出一个大的范围,然后下降到原始列表中,进行精确查找。查询的时间复杂度平均为 O(n/2)。但是当结点数量很大时,查询速度依旧很慢,还是参考二分查找的思路,跳表可以通过在链表上增加若干层索引的方法,让链表拥有近乎二分查找的效率。
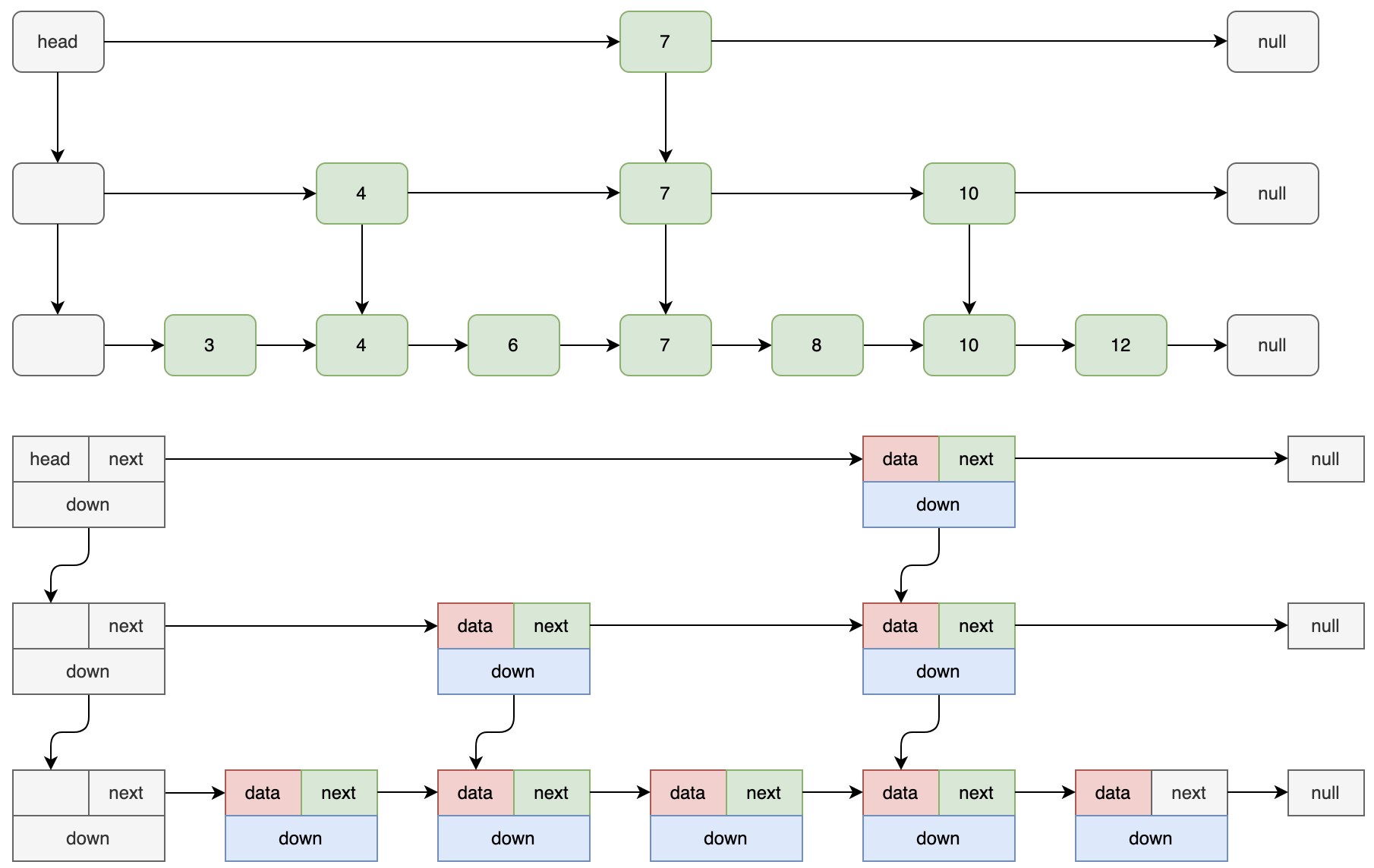
如上图,通过这样的一个数据结构对有序链表进行查找都能近乎二分的性能。在上面维护那么多层的索引,首先在最高级索引上查找最后一个小于当前查找元素的位置,然后再跳到次高级索引继续查找,直到跳到最底层为止,此时已经十分接近要查找的元素的位置了 (如果查找元素存在的话)。由于根据索引可以一次跳过多个元素,所以跳查找的查找速度也随之变快。
对于理想的跳表,每向上一层索引结点数量都是下一层的 1/2. 那么如果 n 个结点增加的结点数量 (1/2+1/4+…) < n。并且层数较低,对查找效果影响不大。但是对于这个结构,完美的结构真的存在吗?大概率不存在的,作为一个链表,少不了增删该查的一些操作。而删除和插入可能会改变整个结构,所以上面的这些都是理想的结构,在插入的时候是否添加上层索引是个概率问题 (1/2 的概率),在后面详细展开。
2.2 方法与实现
定义跳表的结点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
public class SkipNode<T> {
int key;
T value;
SkipNode right;
SkipNode down;
public SkipNode(int key, T value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
|
跳表的定义(跳表的头结点 (head) 的 key 设为 int 的最小值 (一定满足左小右大方便比较))
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
public class SkipList<T> {
SkipNode headNode;
int highLevel;
Random random;
final int MAX_VALUE = 32;
public SkipList() {
random = new Random();
headNode = new SkipNode(Integer.MIN_VALUE, null);
highLevel = 0;
}
}
|
2.2.1 查询
跳表查询任意结点数据的时间复杂度为 O(logn)
查询步骤:
- 从链表顶层索引的第一个结点开始,从左往右搜索,若当前结点的值与查询的值相等,则直接返回当前结点;
- 若不相等,且右侧为空,则说明已经到达当前链表尾部,则只能进入下层索引;
- 若不相等,且右侧不为空,且右侧结点值小于等于待查询的值,则继续向右遍历查询;
- 若不相等,且右侧不为空,且右侧结点大于待查询的值,说明查询结点(若有)就在该索引结点与下一个索引结点,则进入下层索引查询;
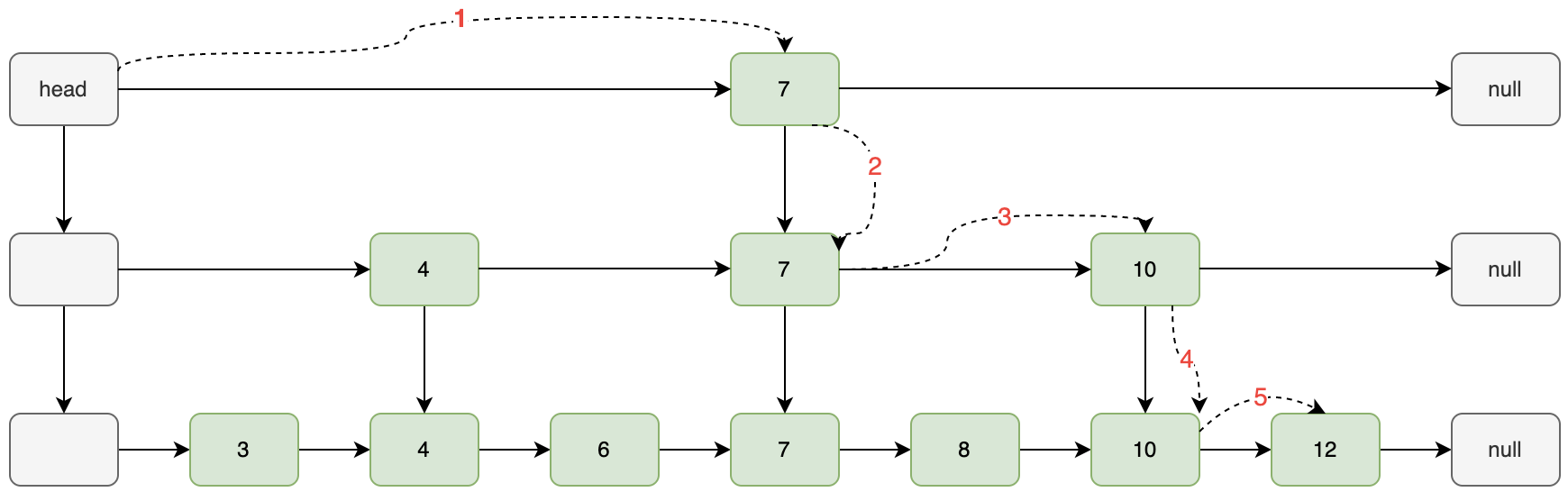
如下图,要求查询值为 12 的结点:
- 从顶层
head 索引出发,右侧下一个结点不为空,且 7 < 12;
- 继续查询下一个结点,为空,则下降到次顶层索引;
- 右侧下一个结点不为空,且
10 < 12 继续向右;
- 继续查询下一个结点,为空,则下降到底层链表;
- 右侧不为空,且小于等于
12,继续向右查询;
- 当前结点等于待查询结点,直接返回该结点;
代码实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
public SkipNode search(int key) {
SkipNode team = headNode;
while (team != null) {
if (team.key == key) {
return team;
} else if (team.right == null) {
team = team.down;
} else if (team.right.key > key) {
team = team.down;
} else {
team = team.right;
}
}
return team;
}
|
2.2.2 删除
跳表插入的时间复杂度为:O(logn)
相比查询操作,删除会更加复杂一些,删除需要改变链表结构以及处理结点之间的联系:
- 删除当前结点以及前后结点的引用;
- 删除当前层的结点后,其它层的也要相应删除;
删除时,需要根据当前链表结点的定义,若是双向链表,则比较方便处理。若是单向链表,则需要保留待删除结点的前一个结点,通过这个结点进行删除操作。删除的具体流程为:
- 若结点右侧为空,则下降到下一层索引;
- 若结点右侧不为空,且右侧结点等于待删除的结点,则先删除结点,在下降到下一层索引,删除下一层索引的结点;
- 若结点右侧不为空,且右侧结点小于待删除的结点,则继续向右遍历;
- 若结点右侧不为空,且右侧结点大于待删除的结点,则下降到下一层索引,继续查询待删除结点;
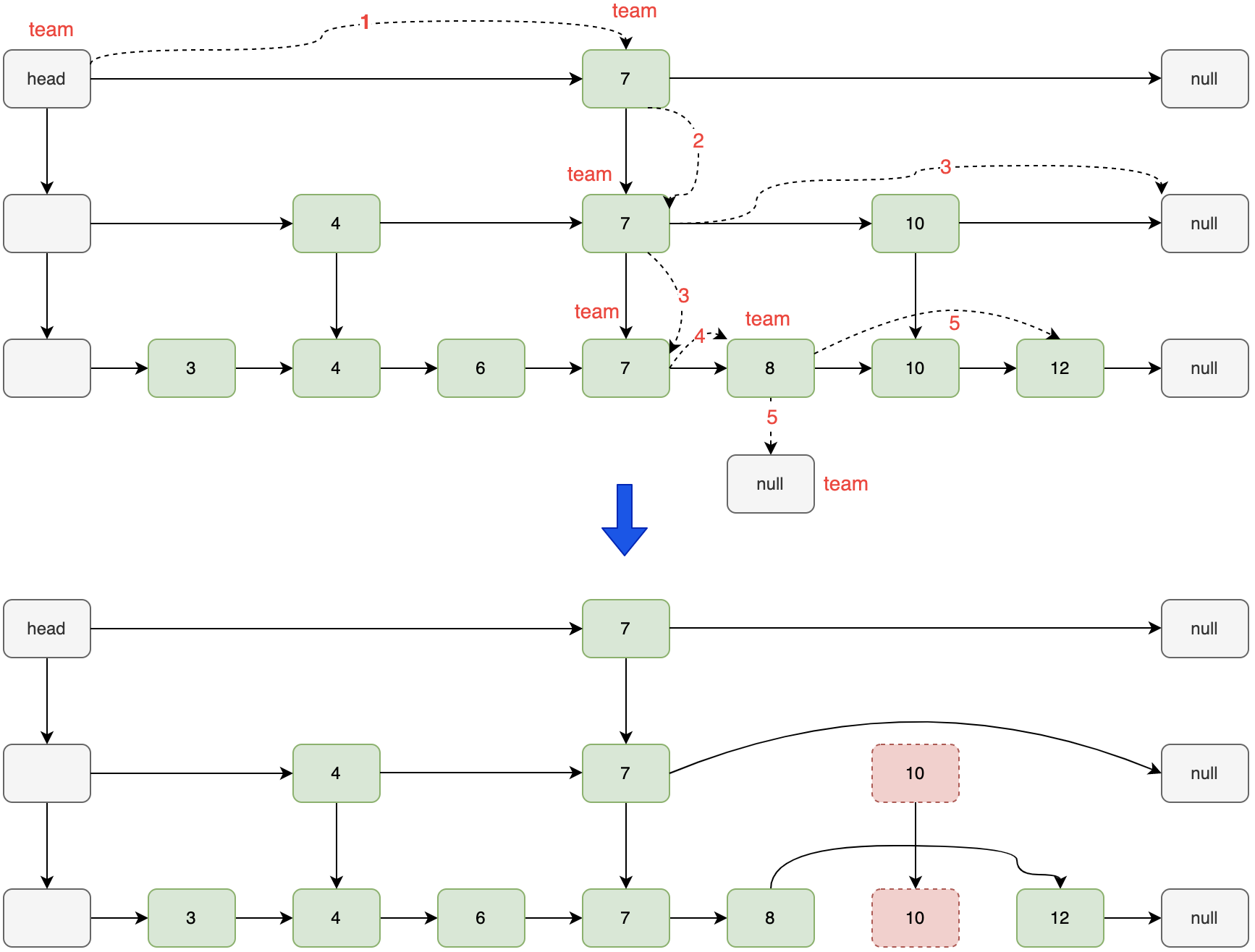
如下图,要求删除值为 10 的结点:
- 从
team = head 出发,7 < 10 向右遍历,
- 右侧为空,下降到下一层索引;
- 右侧为
10 在当前层删除 10,然后继续向下查询下一层的 10 结点,
8 < 10,继续向右遍历;- 右侧为待删除节点
10,继续向下层,但是下层为空,说明删除完毕,返回结果;
代码实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
public void delete(int key) {
SkipNode team = headNode;
while (team != null) {
if (team.right == null) {
team = team.down;
} else if (team.right.key == key) {
team.right = team.right.right;
team = team.down;
} else if (team.right.key > key) {
team = team.down;
} else {
team = team.right;
}
}
}
|
2.2.3 插入
跳表的插入操作时间复杂度为:O (logn)
插入操作是最复杂的,需要考虑上层索引是否需要同时插入,需要插入时,应该插入几层索引?
随着删除和插入操作的进行,跳表肯定是无法持续维护理想的索引结构,因为维护的代价非常高。可以考虑使用随机数来决定是否向上插入索引。
可以分多种做法:
- 先将值插入最底层,从最底层开始向上层索引的方向,产生一个
[0 - 1] 的随机数,如果随机数小于 0.5,则向上插入索引,当插入成功后,再次使用随机数判断是否向上层插入索引,最多可以多层都插入索引;
- 先将值插入最底层,产生一个随机数,若随机数为
K,那么则将在第 K 层插入该节点的索引;
注:一般会设置一个值来限定索引的高度;
插入的流程:
- 和查询一样的步骤,找到待插入的左结点,从底层链表开始插入(需要考虑是否为链表尾部的情况);
- 查完下一层,再考虑是否插入上一层,首先判断当前索引层级数,如果达到限制,则停止插入,否则根据随机数判断是否向上层插入索引(理想的结构是每隔
2 个结点向上建立一个索引);
- 继续步骤
2,直到概率退出或者达到索引数量最大值;
几个关键点
1、具体向上层索引插入时,需要考虑如何找到上一层的待插入节点?
应该需要根据链表节点的定义来判断。若定义的是双向链表,则只需要根据链表的属性寻找上层需要插入的结点;若定义的是单向链表时,当时查询的下降路线的逆序为需要插入结点,最底层也不例外(因为没有匹配值会下降为空时,结束循环),可以使用栈的数据结构来保存查询的路线顺序节点。
示意图:
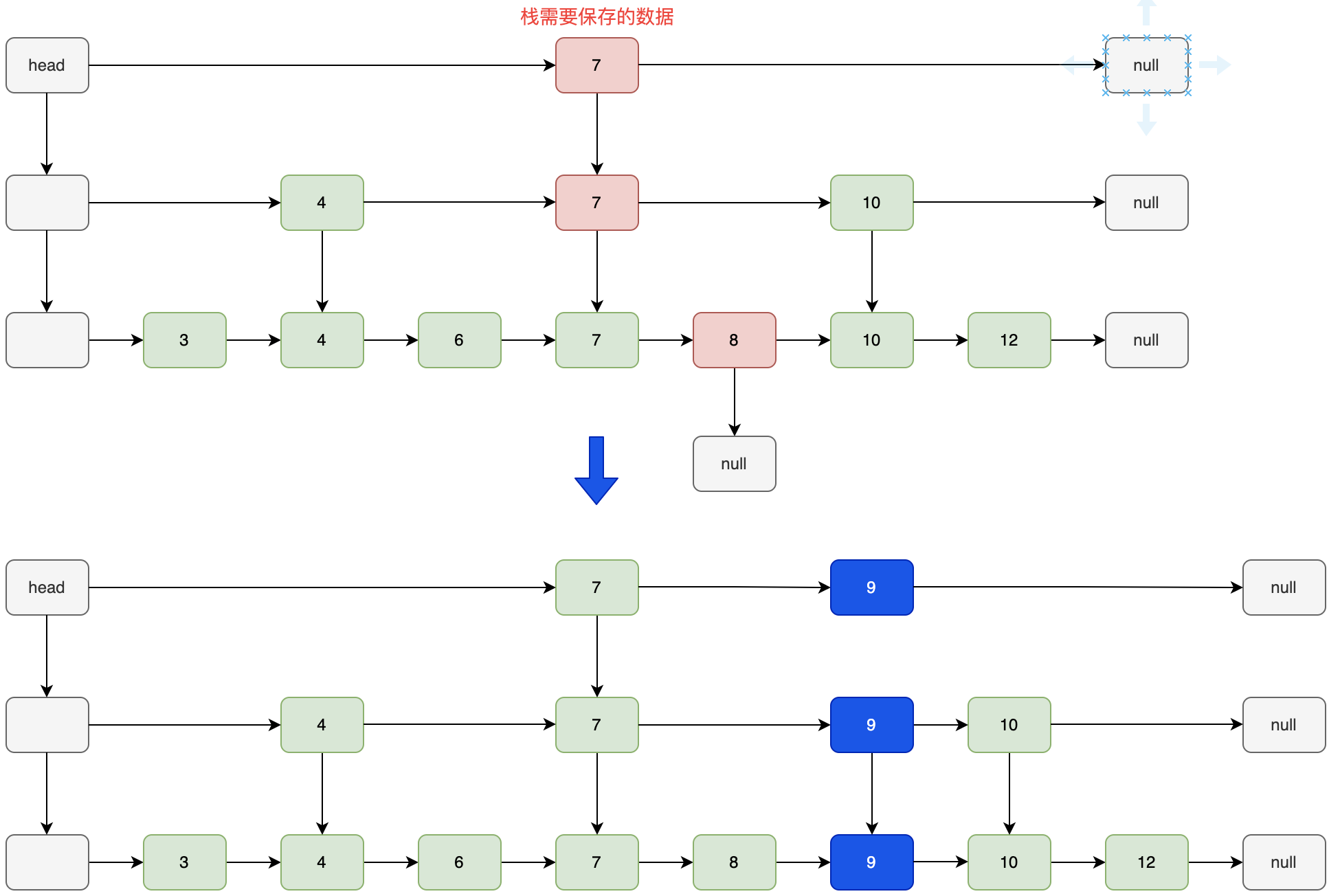
2、如果插入索引达到当前最高索引时,如何继续向上建立索引?
需要改变跳表的 head,新建一个 ListNode 结点作为新的 head,将新 head 的 down 指向老 head,再新将 head 结点加入栈中,后续需要作为插入索引时做准备。
示意图:

代码实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
|
public void add(SkipNode node) {
int key = node.key;
SkipNode findNode = search(key);
if (findNode != null) {
findNode.value = node.value;
return;
}
Stack<SkipNode> stack = new Stack<>();
SkipNode team = headNode;
while (team != null) {
if (team.right == null) {
stack.add(team);
team = team.down;
} else if (team.right.key > key) {
stack.add(team);
team = team.down;
} else {
team = team.right;
}
}
int level = 1;
SkipNode downNode = null;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
team = stack.pop();
SkipNode nodeTeam = new SkipNode(node.key, node.value);
nodeTeam.down = downNode;
downNode = nodeTeam;
if (team.right == null) {
team.right = nodeTeam;
} else {
nodeTeam.right = team.right;
team.right = nodeTeam;
}
if (level > MAX_LEVEL) {
break;
}
double num = random.nextDouble();
if (num > 0.5) {
break;
}
level++;
if (level > highLevel) {
highLevel = level;
SkipNode highHeadNode = new SkipNode(Integer.MIN_VALUE, null);
highHeadNode.down = headNode;
headNode = highHeadNode;
stack.add(headNode);
}
}
}
|
2.3 完整代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
|
public class SkipList<T> {
SkipNode headNode;
int highLevel;
Random random;
final int MAX_LEVEL = 32;
public SkipList() {
random = new Random();
headNode = new SkipNode(Integer.MIN_VALUE, null);
highLevel = 0;
}
public SkipNode search(int key) {
SkipNode team = headNode;
while (team != null) {
if (team.key == key) {
return team;
} else if (team.right == null) {
team = team.down;
} else if (team.right.key > key) {
team = team.down;
} else {
team = team.right;
}
}
return team;
}
public void delete(int key) {
SkipNode team = headNode;
while (team != null) {
if (team.right == null) {
team = team.down;
} else if (team.right.key == key) {
team.right = team.right.right;
team = team.down;
} else if (team.right.key > key) {
team = team.down;
} else {
team = team.right;
}
}
}
public void add(SkipNode node) {
int key = node.key;
SkipNode findNode = search(key);
if (findNode != null) {
findNode.value = node.value;
return;
}
Stack<SkipNode> stack = new Stack<>();
SkipNode team = headNode;
while (team != null) {
if (team.right == null) {
stack.add(team);
team = team.down;
} else if (team.right.key > key) {
stack.add(team);
team = team.down;
} else {
team = team.right;
}
}
int level = 1;
SkipNode downNode = null;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
team = stack.pop();
SkipNode nodeTeam = new SkipNode(node.key, node.value);
nodeTeam.down = downNode;
downNode = nodeTeam;
if (team.right == null) {
team.right = nodeTeam;
} else {
nodeTeam.right = team.right;
team.right = nodeTeam;
}
if (level > MAX_LEVEL) {
break;
}
double num = random.nextDouble();
if (num > 0.5) {
break;
}
level++;
if (level > highLevel) {
highLevel = level;
SkipNode highHeadNode = new SkipNode(Integer.MIN_VALUE, null);
highHeadNode.down = headNode;
headNode = highHeadNode;
stack.add(headNode);
}
}
}
public void print() {
SkipNode teamNode = headNode;
int index = 1;
SkipNode last = teamNode;
while (last.down != null) {
last = last.down;
}
while (teamNode != null) {
SkipNode enumNode = teamNode.right;
SkipNode enumLast = last.right;
System.out.printf("%-8s", "head->");
while (enumLast != null && enumNode != null) {
if (enumLast.key == enumNode.key) {
System.out.printf("%-5s", enumLast.key + "->");
enumLast = enumLast.right;
enumNode = enumNode.right;
} else {
enumLast = enumLast.right;
System.out.printf("%-5s", "");
}
}
teamNode = teamNode.down;
index++;
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SkipList<Integer> list = new SkipList<Integer>();
for (int i = 1; i < 20; i++) {
list.add(new SkipNode(i, 666));
}
list.print();
list.delete(4);
list.delete(8);
list.print();
}
}
|
运行结果:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| > Task :SkipList.main()
head-> 10-> 18->
head-> 10-> 18->
head-> 2-> 10-> 13-> 18->
head-> 1-> 2-> 10-> 13-> 15-> 18->
head-> 1-> 2-> 7-> 8-> 10-> 12-> 13-> 15-> 16-> 18->
head-> 1-> 2-> 3-> 4-> 5-> 6-> 7-> 8-> 9-> 10-> 11-> 12-> 13-> 14-> 15-> 16-> 17-> 18-> 19->
head-> 10-> 18->
head-> 10-> 18->
head-> 2-> 10-> 13-> 18->
head-> 1-> 2-> 10-> 13-> 15-> 18->
head-> 1-> 2-> 7-> 10-> 12-> 13-> 15-> 16-> 18->
head-> 1-> 2-> 3-> 5-> 6-> 7-> 9-> 10-> 11-> 12-> 13-> 14-> 15-> 16-> 17-> 18-> 19->
|
3 总结
- 跳表使用的是空间换时间的思想,通过构建多级索引来提高查询效率,实现基于链表的 “二分查找”,跳表是一种动态的数据结构,支持快速的查找、插入和删除操作,时间复杂度是
O(logn);
- 跳表的空间复杂度是
O(n),不过跳表可以通过改变索引策略,动态的平衡执行效率和内存消耗;
Redis 的有序集合 zset 使用跳表而不使用红黑树的原因主要是,链表能进行范围区间的查询,而树结构不太方便;Java 中 ConcurrentSkipListSet 和 ConcurrentSkipListMap 使用了跳表;
引用






